Understanding Credit Value Adjustment: Essentials for Risk Management
Introduction to Credit Valuation Adjustment
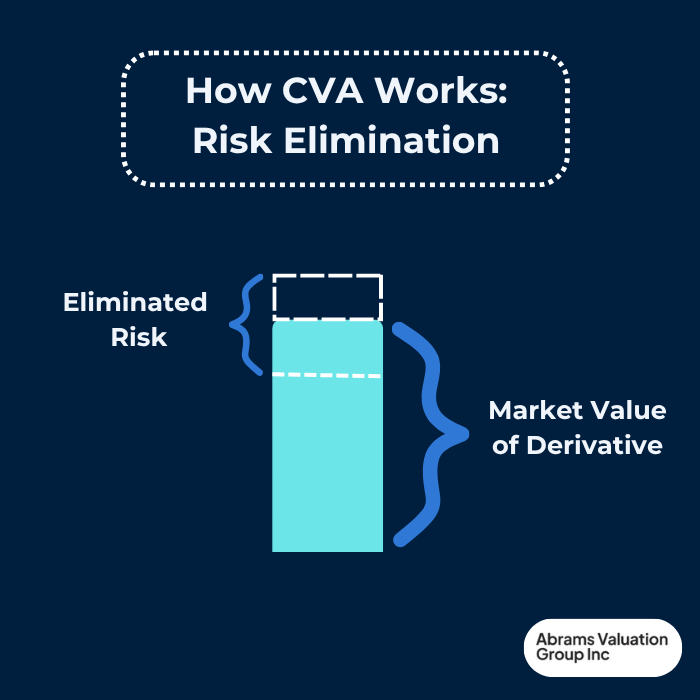
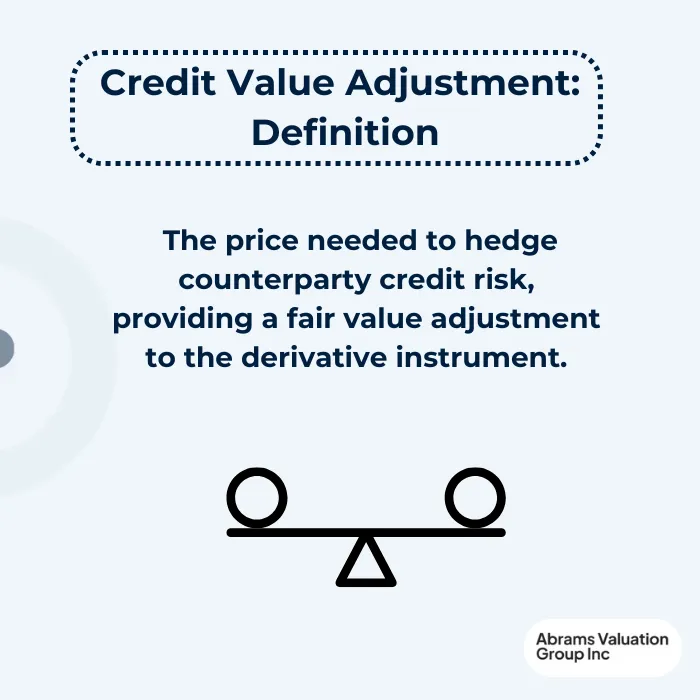
Essentially, CVA reflects the price required to hedge counterparty credit risk, providing a fair-value adjustment to the derivative instrument. Since counterparty credit risk is a significant concern in derivative transactions, CVA serves as a key tool for quantifying and managing this risk. AVGI experts explore the Credit Valuation Adjustment and its impact on asset and business valuation.
Counterparty Credit Risk
Counterparty credit risk arises from the potential default of a counterparty in a derivative transaction, which can result in significant losses for the financial institution involved. This type of credit risk is a critical component of Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA), making a thorough understanding of counterparty credit risk essential for effective CVA management. CVA calculations rely heavily on counterparty credit spreads, and fluctuations in these spreads can substantially impact the valuation. Additionally, market risk factors such as interest rates and volatility also influence counterparty credit risk and, consequently, the CVA. A key element in managing this risk is understanding the default probability of the counterparty, which plays a vital role in CVA calculation and overall counterparty risk management.
CVA Calculation
CVA calculation involves modeling key components such as exposure, default probability, and loss given default to quantify the expected loss arising from counterparty credit risk. The CVA formula integrates these factors—expected exposure, default probability, and loss given default—to accurately determine the credit valuation adjustment. Given the complexity of these calculations, advanced modeling techniques are necessary, often utilizing historical default data and credit spreads to enhance precision. Banks must also calculate CVA capital requirements based on these valuations, ensuring they hold sufficient capital to cover potential losses. It is important to note that regulatory CVA calculations exclude the bank’s own default risk, and banks can leverage eligible external CVA hedges to reduce their CVA capital requirements effectively.


Credit Valuation Adjustment Methods
There are various methods for calculating Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA), ranging from basic approaches to more advanced techniques such as the internal models approach. The choice of method depends largely on a bank’s level of sophistication, available resources, and regulatory requirements. While simpler methods may suffice for some institutions, advanced CVA valuation methods offer greater accuracy but demand significant expertise and infrastructure. Regardless of the approach, fair value accounting standards require that CVA be determined using appropriate valuation techniques to ensure an accurate reflection of counterparty credit risk in the market value of derivative instruments.
Credit Spread and Counterparty Credit Spread
Credit spreads reflect the market’s assessment of counterparty credit risk, making them a vital factor in CVA calculations. Changes in these spreads, driven by shifts in credit quality, can significantly impact the valuation of Credit Valuation Adjustment. Understanding counterparty credit spreads is essential for effective CVA management, as they directly influence the calculation process. Additionally, market risk factors such as interest rates and volatility play a crucial role in affecting both credit spreads and CVA. A comprehensive grasp of default risk is also critical, as it forms a key component of CVA calculation and underpins effective management of counterparty risk.
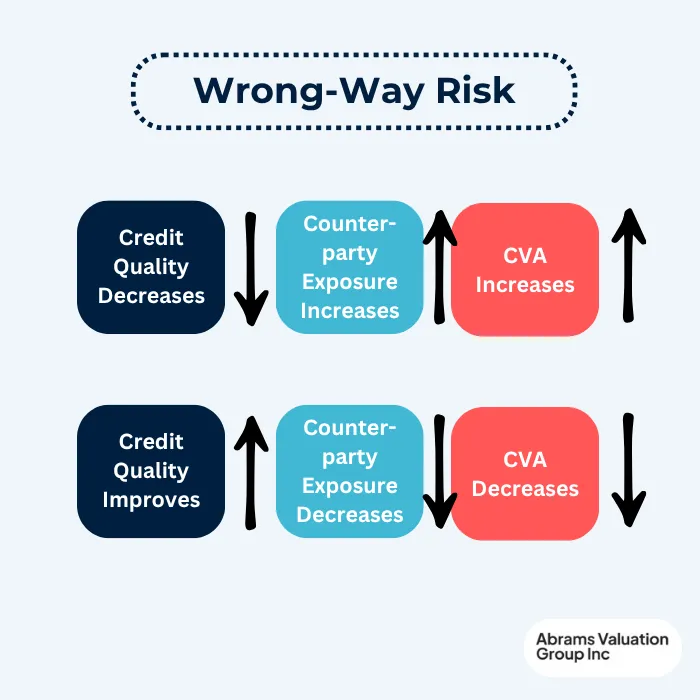
Wrong-way Risk and Adjustment Risk
Wrong-way risk occurs when exposure to a counterparty increases as the counterparty’s credit quality deteriorates, leading to a higher Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA). Adjustment risk refers to the possibility that CVA calculations may not fully or accurately capture the true counterparty credit risk. Effectively managing CVA and counterparty risk requires a clear understanding of both wrong-way risk and adjustment risk. Central to wrong-way risk is the counterparty’s credit quality, as changes in credit quality can significantly influence CVA values. Additionally, market variables such as interest rates and volatility play a crucial role in affecting both wrong-way risk and the overall CVA, making these factors vital considerations in comprehensive risk management.
Risk Management and Hedging
Risk management and hedging are critical components of Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA) and play an essential role in effectively managing counterparty credit risk. CVA hedging typically involves the use of eligible external CVA hedges, which help reduce CVA capital requirements and mitigate potential losses. By employing various hedging and risk mitigation strategies, financial institutions can better control counterparty credit risk exposure. A thorough understanding of the complexities involved in CVA hedging is vital for accurate CVA calculations and effective risk management. Additionally, market risk factors such as interest rates and volatility significantly influence both CVA hedging effectiveness and overall counterparty risk.
Conclusion
Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA) is a fundamental aspect of managing counterparty credit risk in derivative transactions, helping financial institutions accurately assess and price the risk of counterparty defaults. By integrating key components such as expected exposure, default probability, and credit spreads, CVA provides a crucial adjustment to the market value of derivative instruments. Understanding the complexities of CVA calculation, including the impact of wrong-way risk, adjustment risk, and the use of eligible external hedges, is essential for effective risk management and regulatory compliance. Advanced CVA valuation methods enable institutions to better manage their credit risk exposure and capital requirements, ensuring financial stability in an evolving market environment.
For expert guidance on business valuation and to navigate the intricacies of credit value adjustment, contact AVGI today. Our specialists are ready to provide tailored solutions that support your risk management and valuation needs with precision and insight.