Understanding Financial Assets in Valuation
What Are Financial Assets?
A financial asset is a liquid asset that derives its value from a contractual right or ownership claim, including mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and checking and savings accounts. These assets represent claims to receive cash or other financial benefits in the future, making them essential components of a business’s financial portfolio. Financial assets are classified on the balance sheet as either current or non-current, and their values are subject to fluctuations based on market conditions. Abrams Valuation Group Inc. explores the role of financial assets in assessing the value of a business.
Types of Assets
Financial assets represent claims to future cash flows or ownership rights in an entity, distinguishing them from physical (tangible) assets as well as intangible assets.
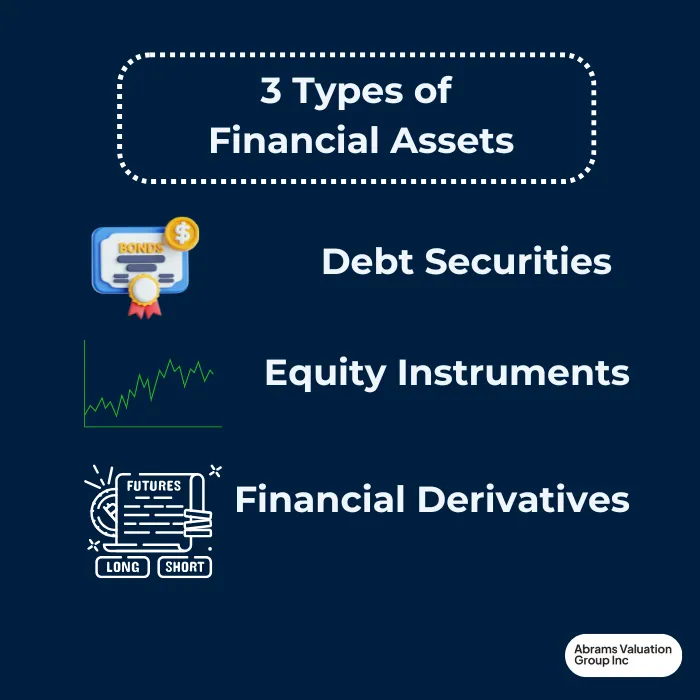
Financial assets can be categorized into 3 main types, including
debt securities
equity instruments
financial derivatives
Debt securities, such as bonds, provide the holder with the right to receive periodic interest payments and the return of principal at maturity. Equity instruments, like stocks, signify ownership in a company and entitle the holder to dividends and voting rights. Financial derivatives, including options and futures, derive their value from underlying assets and are often used for hedging or speculative purposes.
Financial Assets vs Real Assets
Real assets, such as real estate and commodities, are tangible assets with intrinsic value. In contrast, financial assets derive their worth from contractual claims or ownership rights. This contractual nature means their value can fluctuate based on the performance of the underlying asset or market conditions. For example, the market value of stocks can change daily based on investor demand and company performance, while bonds’ prices may be influenced by interest rates and credit risk. Tangible assets, such as property and equipment, but they lack the contractual rights that define financial assets.
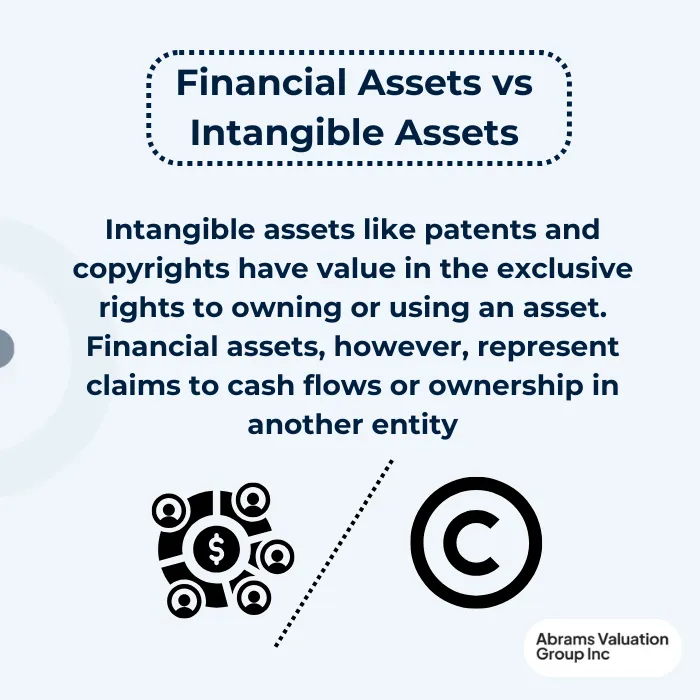
Financial Assets vs Intangible Assets
Intangible assets, such as trademarks, patents, and copyrights, hold value due to the exclusive rights they confer. Still, they do not represent claims to cash flows or ownership in another entity and thus are not classified as financial assets.
Financial Assets vs Capital Assets
Financial assets and capital assets are distinct categories of assets that serve different purposes in finance and accounting. Financial assets represent claims to future cash flows or ownership rights in an entity, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and bank deposits. Their value is derived from contractual rights or ownership claims and can fluctuate based on market conditions and the performance of the underlying entity.
In contrast, capital assets refer to tangible or intangible assets that a business uses to generate income over the long term. These include physical properties like land, buildings, machinery, and equipment, as well as intangible assets such as patents and trademarks. Capital assets are typically held for productive use rather than for immediate sale and are recorded on the balance sheet at historical cost, subject to depreciation or amortization.
The key differences between financial and capital assets lie in their nature and purpose: financial assets are primarily investment vehicles or claims that can be converted into cash, while capital assets are used in the production of goods and services and contribute to the operational capacity of a business. Understanding these distinctions is essential for accurate financial reporting, valuation, and strategic management.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for proper accounting, valuation, and management of assets within a business or investment portfolio. Financial assets play a central role in financial markets and investment strategies, offering opportunities for income generation, capital appreciation, and risk management.
Measurement and Valuation
The measurement and valuation of financial assets depend on the nature and intent of the investment and are typically recorded at fair value. For investments in other entities where the investor has significant influence but not control, the equity method is used to account for these holdings. Debt instruments, such as bonds, are generally recorded at amortized cost and are subject to interest rate risk. Various valuation methods can be applied to financial assets, including the income approach and the market approach, to accurately assess their value based on expected future cash flows and prevailing market conditions.
Assets and Liabilities Management
Effective management of assets and liabilities is crucial for financial institutions and investment companies to minimize the risk of default by matching financial assets and liabilities in terms of maturity and risk. This management process often involves the use of financial instruments, such as derivatives, to hedge against interest rate and credit risks. The primary goal of assets and liabilities management is to maximize profits while minimizing risk, thereby maintaining a stable and healthy balance sheet that supports long-term financial stability and growth.
Investment Accounting
Investment accounting involves recognizing and measuring financial assets, as well as recording investment income and expenses. The accounting treatment varies depending on the type of investment and the level of control or influence the investor holds. Financial assets may be accounted for using the fair value through profit or loss method or the amortized cost method. Additionally, the equity method is applied to investments in associates and joint ventures where the investor has significant influence but does not exercise control.
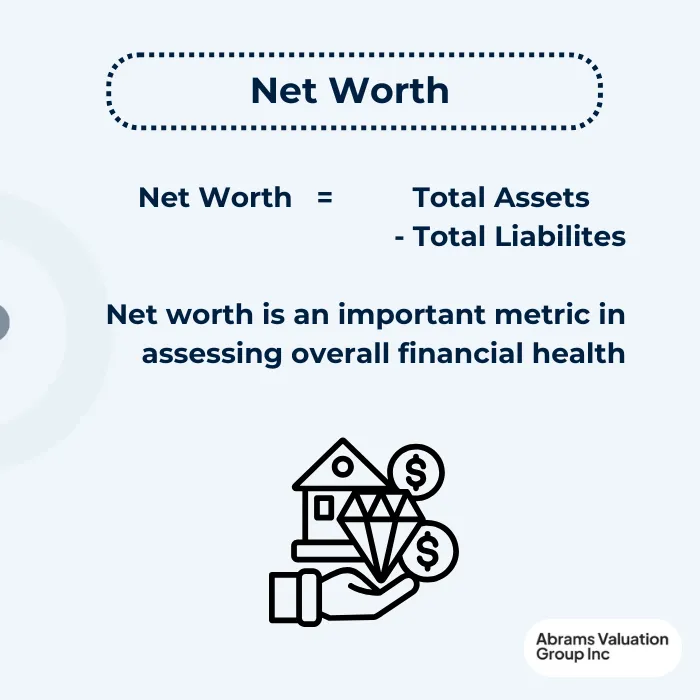
Net Worth and Financial Health
Net worth, defined as the difference between total assets and total liabilities, serves as a key indicator of financial health. Financial assets, including stocks and bonds, contribute significantly to net worth but also carry inherent risks. Effective management of both financial assets and liabilities is essential for maintaining financial stability and achieving long-term financial goals. While a high net worth can provide financial security and flexibility, it requires ongoing management and careful maintenance to sustain and grow over time.
Financial Asset Management Strategies
Financial asset management involves employing various strategies, such as diversification and hedging, to minimize risk while maximizing returns. The selection of financial assets is guided by the investor’s risk tolerance, investment objectives, and the expected return and risk associated with each asset. Management approaches can be either active or passive, depending on the investor’s goals and available resources. Additionally, financial derivatives like options and futures are often utilized to manage risk effectively and enhance potential returns, making them valuable tools in a well-rounded investment strategy.
Risk Management and Diversification
Risk management involves identifying and mitigating various risks associated with financial assets, such as market risk and credit risk. A key strategy in managing these risks is diversification, which entails allocating investments across different asset classes, industries, geographic regions, and sectors to minimize risk and maximize returns. Additionally, hedging strategies, often employing financial derivatives, are used to protect against potential losses and further manage risk effectively.
Financial Planning and Decision-Making
Financial planning involves developing a comprehensive strategy for managing both financial assets and liabilities to achieve long-term financial goals. This process requires careful financial decision-making, which includes evaluating various investment options and selecting the most suitable course of action. Managing financial assets and liabilities effectively must align with the investor’s overall goals and risk tolerance. Additionally, the use of financial models and simulations can provide valuable insights, helping to inform decisions and identify optimal investment strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial assets are a key component of corporate finance and involve a range of different types and risks. Effective management of financial assets and liabilities is crucial for achieving long-term financial goals and maintaining financial health. Employing different strategies, including diversification and hedging, can help to manage risk and maximize returns. Financial assets play an important role in determining the value of the company, as they contribute to the overall financial picture of the company. If you need an expert appraisal of your business’s value, reach out to Abrams Valuation Group, Inc. for a zero-commitment consultation.